The Gig Economy and its Impact on HR Practices
The way we work is changing rapidly. The rise of the gig economy, characterized by short-term, project-based work, is disrupting traditional employment models. This shift presents both opportunities and challenges for HR professionals. This article analyzes current trends in the gig economy, incorporates relevant research, and shares real-world stories to paint a comprehensive picture of its impact on HR practices.
Defining the Gig Economy
Before diving into the impact, let’s establish a common understanding. The gig economy encompasses a variety of work arrangements, including freelancing, independent contracting, on-demand work through digital platforms (e.g., Uber, Upwork), and temporary or contract work. Gig workers are typically self-employed or employed by multiple companies. While they enjoy multiple streams of income and greater flexibility, they often lack the traditional benefits and job security associated with full-time employment. Platforms like Amazon Mechanical Turk are increasingly used for micro-tasks requiring human intelligence, further blurring the lines between conventional work and gig work.
To understand the scale of the gig economy, consider these findings:
A 2023 McKinsey Global Institute report estimates that 20-30% of the global workforce participates in independent work.

The study shows that out of necessity or convenience, regardless, there is an upward trend in people turning to project-based work for a living, primary, secondary, or as a backup in a career landscape marked by high inflation, tech layoffs, and a move towards leaner organizations.
A 2022 study by Upwork predicts that by 2027, the freelance workforce in the United States alone will reach 59 million.
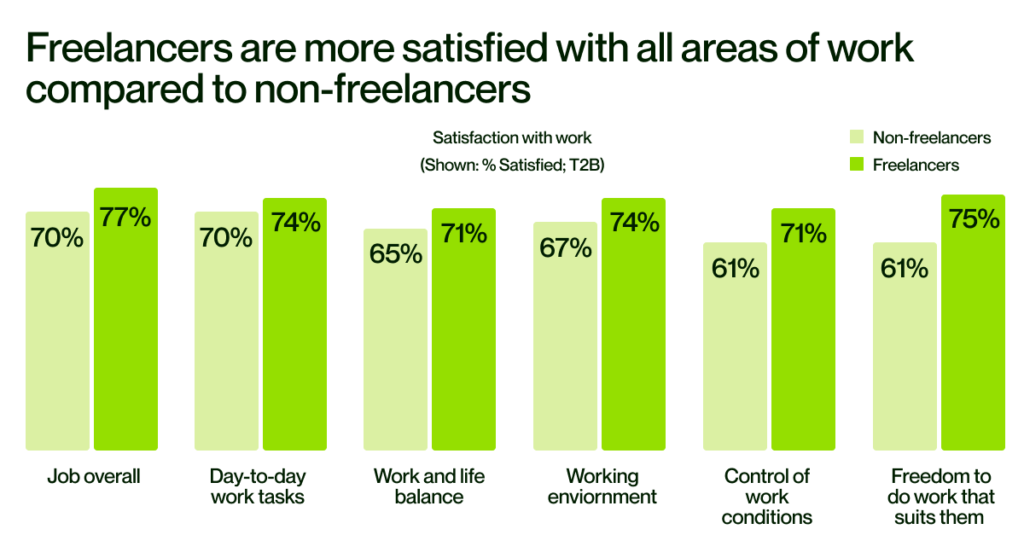
These numbers highlight a growing shift of talent and skill toward the gig economy, presenting organizations with a challenge to update their talent acquisition strategies and infrastructure. (See ANC Global’s Talent Management Solutions)
Impact of Gig Economy on HR Practices
HR professionals need to start leveraging the gig economy instead of treating it as a parallel stream to gain access to a broader range of talent with specialized skills, allowing companies to source expertise for specific projects without the commitment and compensation and benefits expense of a full-time employee.
This calls for the adaptation of recruitment strategies to attract gig workers. Chris Brennan, a performance consultant from Los Angeles, outlines ten rules of thumb for HR to navigate the gig economy.
Treat gig workers with respect and understand their motivations.
Recognize the value gig workers bring to your organization and extend them the same respect for professional boundaries and courtesy as your full-time employees. Foster a culture of open communication where you actively engage with gig workers to understand their motivations, preferred work styles, and availability. By establishing clear communication channels and prioritizing mutual respect, you can build a healthy and productive relationship with your contingent workforce, leading to improved project outcomes and a more engaged talent pool.
Properly classify workers to avoid financial and legal issues
The booming gig economy, while offering flexibility and access to talent, presents complex legal and regulatory challenges for HR professionals. Unlike traditional employment models, managing a gig workforce requires navigating labor laws, tax regulations, and benefits – all while ensuring compliance and fairness.
One of HR’s most critical tasks in the gig economy is meticulously distinguishing between contract workers and full-time employees. Misclassification can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions, including unpaid taxes, employee lawsuits, and hefty fines.
Beyond compliance, HR plays a crucial role in balancing the flexibility of the gig economy with essential worker protections. This could involve:
- Developing clear classification guidelines: Ensuring everyone understands the criteria for classifying workers.
- Implementing robust training programs: Educating managers and gig workers on their rights and responsibilities.
- Utilizing clear and comprehensive contracts: Outlining worker classification, project scope, compensation, and intellectual property ownership.
By prioritizing accurate worker classification and fostering a fair and flexible work environment, HR can unlock the full potential of the gig economy. This can lead to a more diverse talent pool, increased agility for the company, and a positive reputation for ethical gig work practices
Foster a sense of community and belonging for gig workers
Effective HR strategies for the gig economy go further than just managing logistics. Unlike traditional employee relations, which focus on building a sense of belonging among full-time staff, HR needs to create a sense of community and inclusion for gig workers who may not have a physical presence within the organization.
This can be achieved by nurturing a culture of diversity and respect, ensuring gig workers feel valued and integrated. Here are some ways HR can foster this:
- Building Online Communities: Create online platforms or forums where gig workers can connect, share experiences, and collaborate.
- Recognition & Rewards: Implement programs to acknowledge gig workers’ contributions and achievements.
- Clear Communication Channels: Maintain open and consistent communication channels for gig workers to ask questions, raise concerns, and stay informed.
- Learning & Development Opportunities: Offer training or resources relevant to gig workers’ needs and career development.
By prioritizing community and inclusion, HR can cultivate a more engaged gig workforce, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes and higher retention rates. [ANC Global | Employee Engagement & Culture Solutions.]
Offer flexibility and prioritize work-life balance for gig workers
Flexibility and a healthy work-life balance are the siren songs of the gig economy, attracting many skilled professionals. Trying to restrict this very freedom – the core appeal of gig work – is a guaranteed way to lose access to this valuable talent pool. The key lies in understanding their work values and designing a flexible work schedule that caters to them.
Here’s how HR can unlock the power of flexibility:
- Offer Diverse Work Arrangements: Provide a menu of options, including project-based contracts, part-time schedules, and clearly defined hourly work.
- Embrace Asynchronous Communication: Facilitate communication through project management tools and online platforms, allowing gig workers to manage their time effectively.
- Respect Boundaries and Availability: Clearly outline project deadlines and expectations, while respecting gig workers’ pre-existing commitments and preferred work hours.
- Focus on Outcomes, Not Micromanagement: Focus on delivering quality work rather than micromanaging the process. Trust gig workers to manage their time and deliver results on their terms.
By embracing flexibility and respecting the autonomy that gig workers crave, HR can attract and retain top talent. This approach leads to a more engaged and productive gig workforce, ultimately contributing to the success of your projects and the overall competitiveness of your company.
Develop a recruiting strategy specifically for gig workers
While flexibility is a key attraction of the gig economy, HR needs to go beyond simply offering flexible work arrangements. To cultivate a thriving gig workforce, a strategic approach encompassing several key areas is crucial:
- Streamlined Onboarding & Training: Design a smooth onboarding process that familiarizes gig workers with company culture, project expectations, and relevant tools. Offer targeted training opportunities to help them excel in their roles and maximize their contributions.
- Skill-Matching for Project Success: Develop a comprehensive system for matching gig workers’ skill sets with specific project needs. Leverage technology platforms to efficiently filter candidates and ensure the right person is assigned to the right task.
- Robust Communication & Collaboration: Establish clear and consistent communication channels (online platforms, chat tools) to keep gig workers informed, engaged, and connected to the broader team. Foster collaboration by encouraging knowledge sharing and open communication throughout the project lifecycle.
- Recognition & Appreciation: Implement programs to acknowledge the contributions of gig workers and celebrate their achievements. This could include public recognition, incentive programs, or exclusive access to professional development resources.
- Building a Sense of Community: Create opportunities for gig workers to connect with each other and feel valued as part of a larger team. This could involve online forums, social events, or internal newsletters featuring success stories and gig worker spotlights.
By focusing on these areas, HR can create a seamless and engaging experience for gig workers. This fosters a sense of value, belonging, and connection to the organization’s mission, ultimately resulting in higher engagement, better project outcomes, and a more loyal talent pool.
Provide fair compensation and be transparent about payment terms
Attracting and retaining top talent in the gig economy hinges on offering competitive compensation. Here’s why fair pay matters:
- Value Recognition: Compensation should reflect the specific role, skill level, experience, and the unique value gig workers bring to your project. Consider industry benchmarks and current market rates to ensure your pay is attractive.
- Transparency is Key: Be upfront and transparent about payment terms and methods from the very beginning. This builds trust and avoids confusion for gig workers who may manage their finances differently than full-time employees.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Gig Worker Pay Model
It’s important to acknowledge that gig worker compensation often differs from traditional salaried positions. Here’s why:
- Shouldering Benefits and Taxes: Unlike full-time employees, gig workers are typically responsible for their own taxes and benefits (health insurance, unemployment insurance). This can justify higher hourly or project-based rates to reflect the additional costs they incur.
- The Value of Flexibility: Gig workers often prioritize flexibility and autonomy over the stability of a full-time position. Higher pay rates can compensate for the lack of guaranteed income and long-term career progression opportunities.
Crafting a Win-Win Compensation Strategy
By implementing a competitive compensation strategy, you can attract and retain skilled gig workers who deliver exceptional results. Consider these additional tips:
- Offer Multiple Pay Options: Provide flexibility in payment methods (direct deposit, online payment platforms) to cater to gig worker preferences.
- Performance-Based Incentives: Consider incorporating bonuses or incentives tied to achieving specific project milestones to further motivate gig workers.
- Clear Payment Schedules: Establish clear and consistent payment schedules to ensure gig workers receive their compensation promptly.
By prioritizing fair pay, transparency, and flexibility in your compensation structure, you can create a win-win situation for your company and your valuable gig workforce. This fosters a culture of trust and appreciation, leading to a more engaged and productive talent pool.
Give gig economy workers a voice and value their input
Simply offering flexible work arrangements isn’t enough to build a thriving gig workforce. Integrating gig workers into your organizational culture requires a two-way street of communication and feedback.
Here’s how HR can foster a collaborative environment:
- Actively Solicit Feedback: Don’t wait for gig workers to come to you. Actively seek their ideas through surveys, online forums, or post-project interviews. Ask specific questions about project processes, tools, and communication channels.
- Practice Active Listening: Go beyond simply hearing their responses. Truly listen and understand their perspectives. This shows you value their input and builds trust.
- Follow Up and Take Action: Don’t let their feedback fall into a void. Demonstrate that their ideas are valued by providing updates and following through on actionable suggestions. This reinforces open communication and encourages continued participation.
- Set Clear Expectations (Two-Way Street): Communication is a two-way street. While you’re soliciting feedback, it’s also crucial to communicate your expectations clearly. This includes project timelines, deliverables, communication protocols, and performance standards.
By prioritizing open communication and actively soliciting feedback from gig workers, HR can create a more inclusive and collaborative work environment. This fosters a sense of value and belonging for gig workers, leading to higher engagement, improved project outcomes, and a more loyal talent pool.
Recognize and reward gig workers for their contributions
While flexibility is a key attraction of the gig economy, companies need to go further to build a thriving and loyal gig workforce. Two crucial areas to consider are professional development and well-being:
Fostering Growth: Upskilling and Reskilling Opportunities
Gig workers are often responsible for charting their own career paths. Companies can stand out by offering opportunities for upskilling and reskilling:
- Curated Online Resources: Provide access to online learning platforms, industry publications, or webinars relevant to gig workers’ skill sets and project needs.
- Mentorship Programs: Connect gig workers with experienced employees or industry experts who can offer guidance and support.
- Micro-credentials and Certifications: Partner with training providers to offer micro-credentials or certifications that enhance gig workers’ skills and marketability within the gig economy.
By demonstrating a commitment to their professional development, companies can attract and retain top gig workers who are eager to stay competitive in the ever-evolving marketplace.
Promoting Well-being: Addressing Security and Benefits
Gig work can offer flexibility, but it can also come with drawbacks like lack of benefits and job security. HR can explore ways to support gig workers’ well-being:
- Limited Benefits Options (Optional): Consider offering access to discounted health insurance plans, disability insurance, or even paid time off for high-value gig workers.
- Financial Wellness Programs: Partner with financial institutions to offer gig workers access to financial literacy workshops or discounted financial services like tax preparation or retirement planning resources.
- Gig Worker Communities: Create online forums or social events where gig workers can connect, share best practices, and build a sense of community, which can help counteract feelings of isolation often associated with freelance work. (See ANC Global’s Employee Engagement & Culture Solutions)
Building a Sustainable Gig Ecosystem
By addressing both professional development and well-being needs, HR can create a win-win situation for both companies and gig workers. Companies benefit from a more engaged, skilled, and loyal gig workforce, leading to improved project outcomes and overall competitiveness. Gig workers, in turn, feel valued, supported, and empowered to thrive in the gig economy. This ultimately fosters a more sustainable and successful gig ecosystem for everyone involved.
Communicate regularly with gig workers to keep them informed and engaged
The gig economy introduces a unique set of communication challenges for HR. Unlike full-time employees who are immersed in your organization’s culture and communication channels, gig workers are often new to your company’s values and operating procedures. Additionally, they may not have a physical presence within the organization, making it difficult to stay informed about project progress and ensure alignment with your vision.
Breaking Down Barriers: Strategies for Effective Communication
To overcome these challenges and ensure successful project collaboration with your gig workforce, HR can implement several key strategies:
- Clearly Defined Communication Channels: Establish clear and accessible communication channels from the outset. This could include dedicated online platforms, project management tools with built-in chat features, or even a designated team communication app.
- Onboarding and Training: Integrate communication protocols into your onboarding process. Train gig workers on how to use designated communication channels, project management tools, and any relevant communication software.
- Regular Project Updates: Schedule regular check-ins with gig workers, either individually or through group video calls, to discuss project progress, address any concerns, and ensure alignment with project goals.
- Transparency and Open Communication: Practice open and transparent communication. Provide gig workers with clear project timelines, expectations, and access to relevant project information. This fosters trust and reduces confusion.
- Encourage Feedback and Collaboration: Don’t just broadcast information. Encourage gig workers to actively participate in communication by soliciting feedback, fostering collaboration through online forums, and creating a culture where open communication is valued.
Building a Connected Gig Workforce
By implementing these strategies, HR can bridge the communication gap and effectively connect with your on-demand workforce. This fosters a collaborative work environment, ensures project success, and ultimately contributes to a more engaged and loyal gig worker population.
Adapt performance management to focus on short-term objectives and project outcomes
Traditional performance management metrics may not translate well to the gig economy. HR needs to develop new methods to evaluate the performance of contingent workers, focusing on project deliverables and client satisfaction. Additionally, organizations must become adept at utilizing online platforms, building relationships with freelance communities, and crafting compelling project descriptions that cater to the flexibility and autonomy gig workers seek. [ANC Global | Performance & Management]
Table of Contents
ANC Global helps organizations adapt to this transformative landscape through their Talent Management, Performance & Management, Employee Relations, and Employee Engagement & Culture Solutions.
Reach out to info@ancglobalhr.com for a consultation and start adapting your organization for the tidal wave of the gig economy today
Reach Our Global Consultants
Emerging Trends in Gig Economy
So what does the rising gig economy mean for the traditional nine-to-five economy? Only that with technological advances and easier access, many traditional employees are reassessing their preferences and priorities, and choosing instead to take on gig work that affords them the flexibility and work-life balance they sought. Many people no longer want to exist at the whim of a company that could let them go at any moment – they want to live life on their terms. However, these traditional employees bring to the table what contract workers cannot: loyalty and culture. Your company cannot thrive without them. And yet it is less and less possible to attract and retain these loyal workers without rethinking employee retention strategies, redesigning Compensation and Benefits packages, and restructuring work infrastructure (flexibility in schedules and offering hybrid/work-at-home models)
Ethical Implications
The growing Gig Economy brings with it the growing question of the working conditions of the contract workers. the ethical considerations of the gig economy, such as ensuring fair pay and working conditions for gig workers. A recent study conducted by the People’s Association in Grassroots Action and Movements the critical need for enhanced social security measures and regulatory oversight to safeguard the welfare of gig workers in the country. It examines the working conditions faced by app-based cab and delivery drivers in India. The findings emphasize the need for better social security measures and regulatory oversight to protect gig workers’ welfare.
Key findings include:
- Extended working hours: About a third of cab drivers work over 14 hours daily, with 83% exceeding 10 hours and 60% surpassing 12 hours.
- Caste-wise impact: Over 60% of drivers from Scheduled Castes and Tribes work beyond 14 hours, compared to 16% from the unreserved category.
- Financial strain: More than 43% of participants earn less than ₹500 per day or ₹15,000 monthly after expenses, and 76% of delivery persons struggle to meet their financial needs.
- Other challenges: Workers face issues like ID deactivation and customer misbehavior.
The report highlights that unregulated income disparities in the gig economy worsen social inequalities, perpetuating poverty. Prolonged working hours contribute to physical exhaustion, increased risk of accidents, and added stress due to lack of job security and pressure from e-commerce platforms. This study makes evident a need for a regulatory body to safeguard the interests of gig workers.
Conclusion
The rise of the gig economy presents HR with a fascinating paradox: a vast pool of skilled, flexible talent alongside a new set of challenges in attracting, managing, and engaging them. While traditional full-time employees remain crucial, the ability to leverage a contingent workforce strategically can unlock significant advantages for businesses.
Challenges and Opportunities: Where ANC Global Steps In
- Attracting Top Gig Talent: Standing out in a crowded marketplace requires compelling project descriptions, a strong employer brand, and access to pre-vetted talent pools. ANC Global’s expertise in employer branding and access to a network of freelance communities can help you find the right gig workers for the job.
- Performance Management in the Gig Economy: Traditional methods fall short. ANC Global can help you develop new performance frameworks focused on project deliverables, client satisfaction, and skill-based assessments, ensuring project success and a positive gig worker experience.
- Building a Seamless Gig Worker Experience: From onboarding to communication and recognition, fostering a sense of value and belonging is crucial. ANC Global can assist in developing onboarding programs, implementing communication platforms, and designing recognition programs that cater to the unique needs of gig workers.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Misclassifying workers can lead to hefty fines. ANC Global’s legal expertise can help you navigate the complexities of worker classification and ensure compliance with labor laws.
The Future of HR: A Thriving Talent Ecosystem
By overcoming these challenges and harnessing the opportunities of the gig economy, HR can create a thriving talent ecosystem that caters to both full-time employees and the growing contingent workforce. ANC Global can be your partner in this journey, helping you develop a comprehensive gig workforce strategy that fosters engagement, optimizes project outcomes, and ultimately fuels your business success.
This revision expands on the challenges and opportunities, showcasing how ANC Global’s services can address them. It also emphasizes the future-oriented approach ANC Global offers to help HR thrive in the gig economy.
- Employee Disengagement: Your Fault or the General Environment’s?
- How to Develop a Strategic Workforce Plan: A Guide for HR Directors
- How Your Head of HR Helps the CEO Win: The Strategic Edge No One Talks About
- Is AI Killing Creativity in your employees?
- Top 3 Issues on the Minds of MENA Board Directors in 2025
